10-Second Summary
Which cloud service is best for your business?
- IaaS: Best for businesses needing customizable infrastructure and technical control.
- PaaS: Ideal for software development without the hassle of infrastructure management.
- SaaS: Perfect for easy-to-use, ready-made software solutions with minimal technical involvement.
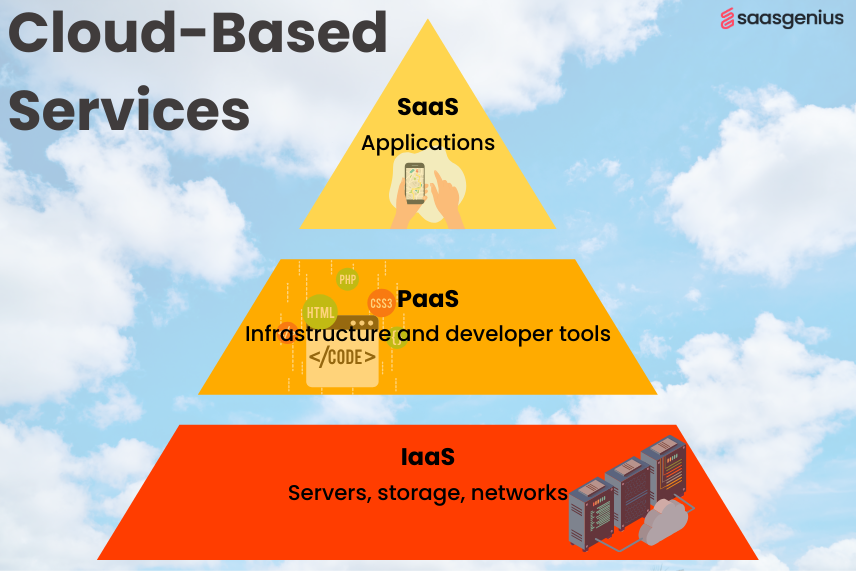
Overview of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
This table provides a clear and concise overview of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS and highlights their key features and typical use cases.
| Service Type | Core Elements | Flexibility | Ideal For | Example Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) | Servers, storage, networking | Scalable up or down | Businesses needing control over their infrastructure without physical hardware investment | Data storage, paying only for used space |
| PaaS (Platform as a Service) | Infrastructure plus development tools | Supports the entire development process | Developers building applications without managing infrastructure | Developing a web application, simplifying backend management |
| SaaS (Software as a Service) | Complete software solutions hosted on the cloud | User-friendly, no maintenance required | Accessible through the internet, usually on a subscription basis | Using an email service like Gmail, fully managed by the provider |
Understanding Cloud Services
Choosing the right cloud service — be it SaaS, PaaS or IaaS — is an important decision for any company. This decision depends on various factors unique to the needs of your business. We will demystify these services so that you can make an informed decision that is perfectly aligned with your business goals.
But first, what are IaaS, PaaS and SaaS?
What Are They?
- IaaS: Think of it as the foundation. It provides the basic infrastructure – servers, storage, and networking. It’s like renting the land and materials to build your house.
- PaaS: This is the next level. In addition to the infrastructure, it also provides the platform – tools for development. It’s like having the land, the materials and a basic structure for your house.
- SaaS: The most comprehensive variant and offers a complete product that can be used immediately. It’s like renting a fully furnished house.
Why It Matters
Each service is suitable for different phases and types of projects. Understanding them will help you make informed decisions and save time and resources.
In the next chapters, we will go into more detail about the individual services and help you to find out which service best suits your needs.
Comparative Analysis: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
Now that we know what IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS are, let’s look at the intricacies of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS and examine important aspects such as control, management overhead, customization, cost, ease of use, and scalability.
This comparison will give you a better understanding of each service and help you find the best solution for your individual business and operational needs. Let’s take a side-by-side look at these cloud services and highlight their different features and benefits for your business.
| Feature | IaaS | PaaS | SaaS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | High control over the infrastructure. | Moderate control, mainly over the application and data. | Limited control, mainly user-specific settings. |
| Management Overhead | Higher, as you manage more of the infrastructure. | Reduced, as the platform is managed for you. | Minimal, as everything is managed by the provider.Customization. |
| Customization | Highly customizable infrastructure. | Customizable at the application level. | Limited customization options. |
| Cost | Pay for what you use; can vary significantly. | Predictable costs, but can escalate with additional services. | Typically a subscription model, steady cost. |
| Ease of Use | Requires technical knowledge to set up and manage. | Easier for developers, less infrastructure management. | User-friendly, no technical skills needed for setup. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable, manual scaling. | Scalable, with some platform-imposed limitations. | Scalability varies, usually easy to scale. |
Determining Factors for Choosing a Service
Choosing the right cloud service for your business requires a careful evaluation of several key factors. These include the technical expertise in your organization, the size and nature of your business, cost, scalability, and security considerations.
Each of these factors plays a crucial role in determining the most suitable cloud service for your specific requirements and ensuring that your choice not only meets your current needs but also supports your long-term business goals.
Let’s take a look at some of the most important factors for choosing IaaS, PaaS or SaaS for your business.
| Factor | IaaS | PaaS | SaaS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technical Expertise Required | High – Ideal for teams with strong technical skills in managing and customizing infrastructure. | Moderate – Suitable for developers who focus on software creation with less emphasis on infrastructure. | Low – User-friendly with no need for technical skills for operation or maintenance. |
| Business Size and Type | Large enterprises with specific needs and capabilities to manage complex systems. | Businesses with a focus on software development, beneficial for mid-sized to large companies. | Small to medium-sized businesses or those requiring standard applications without customization. |
| Cost | Pay-as-you-go model, variable costs depending on usage. | Predictable costs, scalable with additional services. | Fixed subscription fees, easy for budget planning. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with manual adjustments. | Scalable, subject to platform capabilities and limitations. | Scalability varies, generally easy and managed by the service provider. |
| Security | User is responsible for most of the security measures. | Mixed responsibility; platform security is managed by the provider, application security by the user. | Fully managed by the provider, minimal user responsibility. |
Common Use Cases For IaaS, PaaS, And SaaS In Different Industries
Different industries use IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS for different purposes. Here are some common use cases for each cloud service model. These examples can help you recognize which option is right for you.
IaaS
- E-commerce companies use IaaS to host their websites and manage their online stores.
- Healthcare organizations use IaaS to store and manage patient data securely.
- Gaming companies use IaaS to host their games and manage their online communities.
PaaS
- Software developers use PaaS to build, test, and deploy applications without worrying about infrastructure management.
- Startups use PaaS to quickly develop and launch new products and services.
- Enterprises use PaaS to build and manage microservices and APIs.
SaaS
- Small businesses use SaaS for accounting, customer relationship management (CRM), and email marketing.
- Education institutions use SaaS for learning management systems (LMS) and student information systems (SIS).
- Human resources departments use SaaS for applicant tracking, performance management, and employee engagement.
- Real estate companies use SaaS for property management, client interactions, and market analysis.
Pros and Cons of Each
In this section, we look at the pros and cons of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS and provide a balanced overview to help you make a decision aligned with your business goals.
IaaS
Pros
![]() Customizable
Customizable![]() Highly scalable
Highly scalable![]() Control over the infrastructure.
Control over the infrastructure.
Cons
![]() Requires technical expertise
Requires technical expertise ![]() Higher management overhead.
Higher management overhead.
PaaS
Pros
![]() Streamlines development
Streamlines development![]() Reduces the complexity of managing infrastructure
Reduces the complexity of managing infrastructure![]() Efficient for application development
Efficient for application development
Cons
![]() Less control over the underlying infrastructure
Less control over the underlying infrastructure ![]() Potential limitations set by the platform
Potential limitations set by the platform
SaaS
Pros
![]() User-friendly
User-friendly![]() No maintenance or installation required
No maintenance or installation required![]() Straightforward subscription model
Straightforward subscription model
Cons
![]() Least customizable
Least customizable![]() Rely on the provider for performance and security
Rely on the provider for performance and security
Examples of IaaS, PaaS, And SaaS In Different Industries
IaaS examples
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) – AWS is the largest and best-known cloud computing provider. It offers a wide range of IaaS services, including computing power, storage space, networks, and databases.
- Microsoft Azure – Azure is another major cloud computing provider. It offers a similar range of IaaS services to AWS.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP) – GCP is the third major cloud computing provider. It offers a more specialized range of IaaS services that focus on machine learning and artificial intelligence.
PaaS examples
- Google App Engine – App Engine is a PaaS platform that enables developers to build and deploy web applications without having to worry about managing the underlying infrastructure.
- AWS Elastic Beanstalk – Elastic Beanstalk is a PaaS platform that enables developers to deploy web applications on AWS without having to worry about managing the underlying infrastructure.
- Heroku – Heroku is a PaaS platform that is popular for deploying Ruby on Rails applications.
SaaS examples
- Salesforce – Salesforce is a CRM (Customer Relationship Management) SaaS platform.
- Dropbox – Dropbox is a SaaS platform for sharing files.
- Figma – Figma is a web-based design platform that allows users to create and collaborate on designs, such as user interfaces, prototypes and visual mockups.
Key Takeaways
When navigating the complexities of cloud computing, it’s important to understand the nuances of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
IaaS offers extensive customization and control and is ideal for companies with specific infrastructure requirements. PaaS strikes a balance by facilitating software development without the complexity of infrastructure management. SaaS offers a user-friendly, out-of-the-box software solution that is perfect for organizations seeking simplicity and minimal technical involvement.
As you can see, each model offers different benefits and limitations, so the choice depends heavily on your company’s specific needs, technical capabilities and long-term goals.
Author
Methodology
- Who?
We are SaaS experts: Our specialists constantly seek the most relevant information to help support your SaaS business. - Why?
We are passionate about users accessing fair SaaS pricing: We offer up-to-date pricing data, reviews, new tools, blogs and research to help you make informed SaaS pricing decisions. - How?
With accurate information: Our website manager tests each software to add a Genius Score using our rating methodology to each product. Our editorial team fact-check every piece of content we publish, and we use first-hand testing, value metrics and leading market data.
