If you’ve ever found yourself gravitating towards the middle option on a menu or considering an upgrade for just a slight price increase, you’ve probably experienced the magic of decoy pricing. It’s a subtle yet powerful technique that businesses employ to shape consumers’ decisions. And its influence is more pervasive than you might think.
This article explores everything you need to know about a decoy pricing strategy, including its meaning, benefits, and potential drawbacks. You’ll also learn the psychology behind this strategy and examine real-world examples of brands using it.
In the end, you’ll be able to decide if decoy pricing is right for your business and how you can leverage it to boost sales and increase your business revenue.
Decoy Pricing Definition
Decoy pricing, also known as “asymmetric dominance,” is a strategic pricing technique businesses use to influence consumer choices and nudge them towards a particular option.
It involves introducing a third, less appealing product or pricing tier alongside two others. This third option, known as the “decoy,” is intentionally designed to make one of the original options more attractive to consumers.
Using a decoy allows businesses to manipulate consumer perceptions of value and encourage them to choose the option that the brand desires. This psychological pricing strategy capitalizes on how people make decisions when faced with multiple choices.
MORE: How do trial pricing strategies work?
How Does it Work?
Decoy pricing relies on the principles of cognitive bias and decision-making psychology. When consumers are presented with multiple options, they tend to compare and evaluate them based on their perceived value. This is where the decoy comes into play.
The decoy is strategically positioned to make one of the other options seem more appealing. One psychological phenomenon that contributes to the effectiveness of decoy pricing is known as the “compromise effect.”
The compromise effect suggests that when faced with multiple options, consumers are more likely to choose the middle option when there is a third option that is intentionally designed to be less attractive. This is because the presence of the decoy makes the middle option appear like a reasonable compromise between the extremes.
National Geographic conducted an informal experiment with popcorn at a movie theater. At first, they offered small and large popcorn bags for $3 and $7, respectively. Most customers went for the small packages until they introduced a decoy — a medium package of $6.5.
Then everyone started going for the large popcorn. When asked about the reason for choosing the large package, a participant said “The large looks like such a better value than the medium… it’s just 50 cents.”

Pros and Cons of Decoy Pricing
Decoy pricing offers several benefits to businesses. At the same time, you have to consider some of its drawbacks. Here are some pros and cons of this pricing technique:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Decoy pricing strategically nudges consumers towards specific options, increasing the likelihood of a desired outcome for the business. | Some critics argue that decoy pricing manipulates consumer choices and takes advantage of cognitive biases. |
| Businesses can increase consumer interest by creating a reference point for comparison and making desired options appear more valuable. | Some customers might feel manipulated when they become aware of the decoy strategy, and this perception can erode their trust in the business. |
| The presence of a decoy simplifies choices for consumers. This can reduce decision fatigue and increase the likelihood of a purchase. | Designing effective decoys requires careful analysis and understanding of consumer behavior. And many businesses don’t have the resources for this process. |
| Positioning a premium option alongside a decoy increases the likelihood that consumers might opt for the higher-priced choice. | If not executed well, the presence of a decoy might confuse consumers and deter them from making a choice. |
MORE: Freemium business model
Decoy Pricing Examples
To illustrate the effectiveness of decoy pricing, let’s look at some real-life examples.
1. Apple
Apple typically offers multiple models with different price points, such as the standard iPhone, the iPhone Pro, and the iPhone Pro Max. The Pro Max model acts as a decoy because it is priced significantly higher than the other models. This makes the standard iPhone and the Pro model appear more reasonably priced in comparison.
Apple also uses the decoy effect in its bundling strategy. For example, when purchasing a MacBook, customers are given the option to add additional accessories or software at a discounted price.
These bundles act as decoys because they offer perceived value, making customers more likely to choose the bundle rather than purchasing individual items separately.
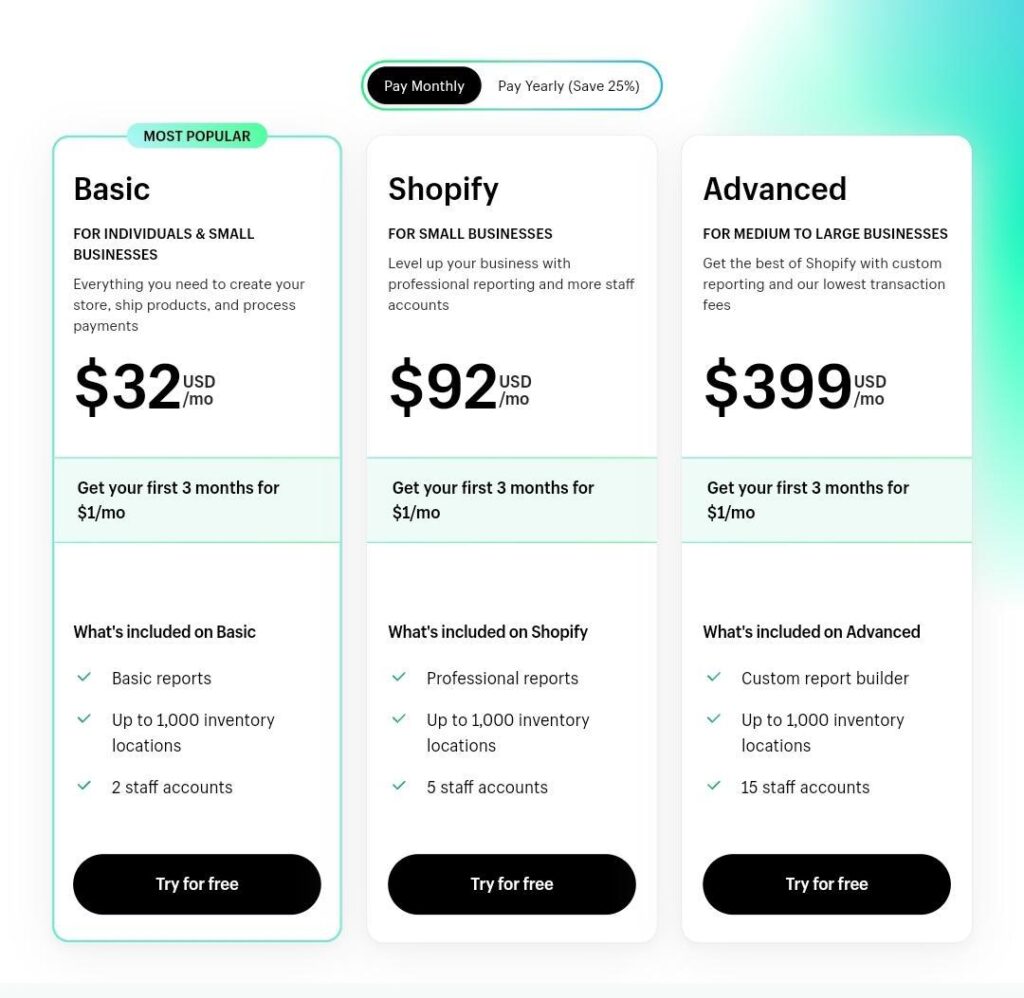
2. Shopify
Shopify’s initial two pricing levels are at just below $100, whereas the third alternative costs notably higher, at $399. Even a feature-to-feature comparison doesn’t completely account for the discrepancy in cost. Shopify introduced the advanced plan as a decoy.
3. The Economist
The Economist, one of the top business magazines in the world, is a classic example of an online subscription service using a decoy pricing strategy. It offers the digital versions of its media at $20.90/month, and a combination of both its print and digital versions at $27.50/month. Most people would opt for the $27.50 subscription, after all, it’s just $6.6 extra for the print version advantage.
MORE: What is penetration pricing?
3 Ways to Implement an Effective Decoy Pricing Strategy
Implementing an effective decoy pricing strategy requires careful consideration and planning. Here are some steps to help you get started:
1. Understand Your Target Market
The first step in implementing a decoy pricing strategy is to understand the target market and their preferences. You need to conduct market research and analyze consumer behavior to determine which options would be most appealing.
You also have to study your competitors. What packages or offers are common in your industry? Use these data to create a data-driven customer journey and hypothetical pricing options.
2. Design the Decoy
After studying your target market and learning the norms in your industry, create three pricing options: a low-priced option, a high-priced option, and the decoy option.
The low-priced option should be attractive enough to capture the attention of price-sensitive consumers, while the high-priced option should be positioned as a premium offering with additional features or benefits.
Finally, the decoy option should be priced slightly higher than the middle option but have fewer features or benefits. This creates a clear distinction between the options and makes the middle option appear more appealing.
MORE: What is prestige pricing?
3. Test and Refine
Implement your decoy pricing strategy on a small scale and monitor the results. At this point, you should optimize your pricing page or material to highlight the best offer. The middle option should be highlighted as the best value for money and positioned prominently in marketing materials.
It’s also important to regularly evaluate and adjust your decoy pricing strategy based on customer feedback and market trends. Keep track of sales data and customer preferences to identify any areas for improvement or potential adjustments in pricing.
MORE: What is usage-based pricing?
Is Decoy Pricing Right for Your Business?
Decoy pricing can be a powerful tool for influencing consumer behavior and increasing sales. However, it is not suitable for every business or product.
Before implementing a decoy pricing strategy, carefully consider your target market, product offerings, and goals. Conduct market research, test different pricing strategies, and analyze the results to determine if decoy pricing is the right approach for your business. You can also explore other pricing strategies, like loss leader pricing.
Remember, pricing strategies should be flexible and adaptable. As consumer preferences and market conditions change, you may have to reassess and adjust your pricing strategy accordingly.
For more information on SaaS pricing and pricing strategies, visit our SaaSGenius pricing site.
Related Posts
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Author
Methodology
- Who?
We are SaaS experts: Our specialists constantly seek the most relevant information to help support your SaaS business. - Why?
We are passionate about users accessing fair SaaS pricing: We offer up-to-date pricing data, reviews, new tools, blogs and research to help you make informed SaaS pricing decisions. - How?
With accurate information: Our website manager tests each software to add a Genius Score using our rating methodology to each product. Our editorial team fact-check every piece of content we publish, and we use first-hand testing, value metrics and leading market data.